Writing Classes
In this unit, you will create your own classes with methods to perform required operations. Complicated methods will be divided into simpler, supporting methods. Some methods will be overloaded and become polymorphic.
Objectives
- Define classes that act like blueprints for new objects, made of variables and methods.
- Explain encapsulation and Java modifiers.
- Explore the details of method declarations.
- Review method invocation and parameter passing.
- Explain and use method overloading.
- Learn to divide complicated methods into simpler, supporting methods.
- Describe relationships between objects.
|
Example Source Files (What do these programs do & how do they work?):
CountFlips.java Coin.java Account.java ManageAccounts.java Die class DifferencecodeProject2 GamblingCodeProject3 SixCodeProject4 AlarmClassCodeProject5 PigLatinProject6MainMethod |
Classes And Objects Notes Page
Writing Classes Headings Guide UML Diagram Structure Notes Blank UML Template |
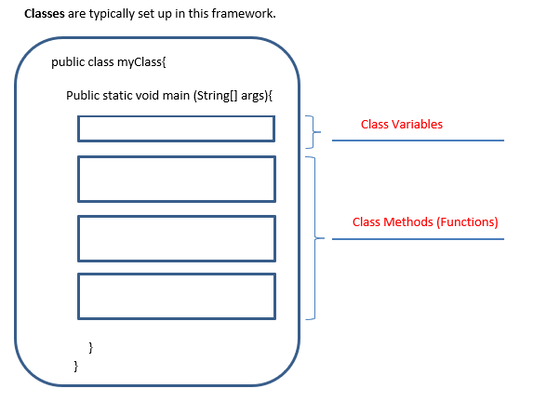
About Class Structures
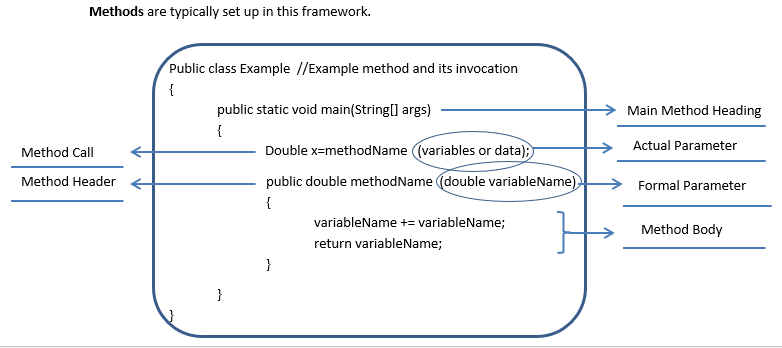
Notice that the name or value of the actual parameter takes on the name of the formal parameter when it is used within the method body. In this generic example, any variables or data put in the method call would take on the name "variableName" in the method when it is used. It's the same value but has a different identifier.
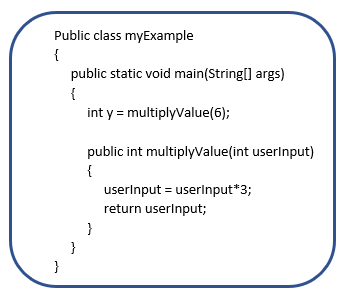
Here's an actual example:
Here's an actual example:
|
As you can see, the actual parameter of 6 is assigned to the formal parameter "userInput" and then used in the method when it is run. When complete, the variable y would have a value of 18.
Note that the variable "userInput" can only be used within the method "multiplyValue" because it has limited SCOPE. If you need a variable to be used throughout the program, you need to create it with GLOBAL SCOPE by declaring it outside the method. |
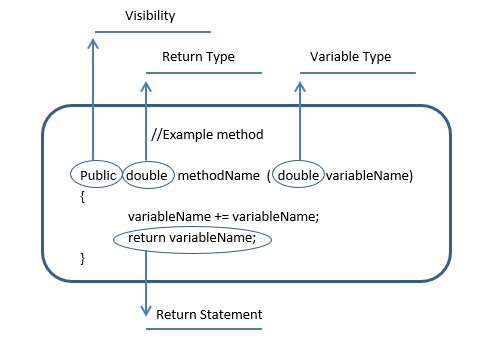
The diagram below shows the parts of an example method:
In a method, the return type listed in the method header MUST MATCH the return type specified in the body of the method. Also, if a return type is listed in the header, there must be a return statement in the body. Conversely, you cannot put a return statement in the method body if no return type is listed in the header. Finally, if you don't want a return type, you must put the word "void" as the return type in the method header.